Market Overview 2025-2033
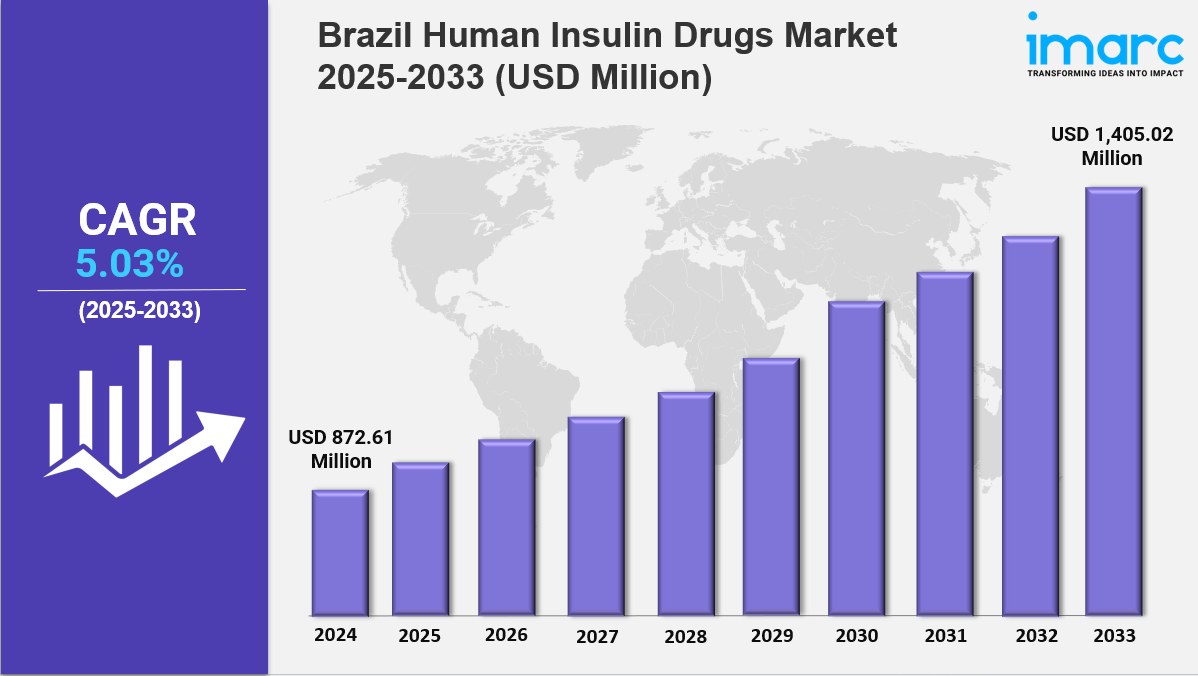
The Brazil human insulin drugs market size reached USD 872.61 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 1,405.02 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.03% during 2025-2033. The market is growing due to rising diabetes prevalence, increased health awareness, and demand for affordable insulin therapies. Growth is driven by biosimilars, local manufacturing, and healthcare initiatives, making the industry more accessible, evolving, and competitive
Key Market Highlights:
✔️ Strong market growth driven by increasing diabetes prevalence and improved healthcare access
✔️ Rising demand for affordable and effective insulin therapies
✔️ Expanding government support and awareness programs promoting early diagnosis and diabetes management
Request for a sample copy of the report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/brazil-human-insulin-drugs-market/requestsample
Brazil Human Insulin Drugs Market Trends and Drivers:
Brazil’s public healthcare system, Sistema Único de Saúde (SUS), is key for insulin access. It provides free or subsidized human insulin to over 75% of people. However, in 2024, budget issues have strained SUS. This has caused supply shortages and delays in procurement. To address this, the government has increased partnerships with local manufacturers like Biomm and EMS. This aims to boost production of biosimilar human insulin and lessen dependence on imports.
At the same time, regulatory reforms are in place. These reforms create faster approval pathways for biosimilars. The goal is to cut costs while keeping quality high. Still, regional disparities exist. Rural areas struggle with distribution challenges. Meanwhile, private companies are filling gaps in public coverage. They offer premium-priced analog insulins, leading to a two-tier market. This creates tension between affordability and innovation. The Brazilian insulin market is changing rapidly as biosimilars gain popularity. This shift is due to cost-saving policies and the expiration of patents for original drugs. In 2024, biosimilars made up almost 40% of human insulin sales, rising from 25% in 2022. Companies like BioNovis and Libbs Pharma are expanding their offerings.
Price competition has grown. Biosimilar products are priced 30–50% lower than original drugs. This forces multinationals like Novo Nordisk and Sanofi to adjust their strategies. They are now focusing on value-added services, such as patient education platforms. However, some challenges remain. Many doctors are hesitant, and patients are skeptical about the effectiveness of biosimilars. The National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) has introduced stricter bioequivalence standards to increase confidence. Still, access to these products varies widely across different socioeconomic groups.
This reflects gaps in healthcare literacy. Brazil’s tech-savvy cities are increasing the need for integrated diabetes management. This combines insulin therapies with digital tools. Startups like Glic and HealthTech Connect launched AI-powered platforms in 2024. These platforms sync insulin dosing data with glucose monitors for real-time adjustments. Public-private partnerships are testing these tools in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. Their goal is to cut hospitalization rates for diabetes complications by 20%. After the pandemic, telehealth adoption has improved insulin adherence in remote areas. SUS is now offering virtual consultations for prescription renewals. However, infrastructure issues, like unreliable internet in rural areas, limit growth.
Manufacturers are addressing this by adding QR codes to insulin packaging. These codes connect patients to instructional videos, helping to close the education gap. The Brazil human insulin drugs market faces many challenges. Regulatory changes, demographic shifts, and tech advances shape its landscape. Diabetes affects nearly 16% of adults, the highest in Latin America. This drives strong demand for insulin, especially in cities with sedentary lifestyles and changing diets. In 2024, reforms will speed up ANVISA approvals for biosimilars. This helps local producers enter the market faster, but quality control issues can still cause delays. Another trend is a focus on preventive care.
Government campaigns promote early diagnosis to reduce complications, which make up 60% of diabetes costs. In mid-2024, tiered pricing models were introduced. Multinationals now offer discounts for bulk purchases by state governments, which eases fiscal burdens. At the same time, environmental sustainability is becoming a key factor. Companies like Biomm are adopting carbon-neutral production to support Brazil’s climate goals. Patient advocacy groups are also gaining power. They lobby for broader coverage of analog insulins under SUS, which currently focuses on human insulin due to costs.
Looking ahead, the market’s path depends on balancing equity and innovation. Biosimilars and digital tools can provide cost savings and better outcomes. However, challenges like uneven healthcare access and economic instability could worsen disparities. Strategic partnerships among regulators, manufacturers, and tech providers will be essential. These collaborations should ensure that growth in Brazil’s insulin market benefits all patients fairly.
Brazil Human Insulin Drugs Market Segmentation:
The report segments the market based on product type, distribution channel, and region:
Study Period:
Base Year: 2024
Historical Year: 2019-2024
Forecast Year: 2025-2033
Breakup by Product Type:
- Human Insulin
- Basal Insulin
- Bolus Insulin
- Insulin Combinations
- Biosimilar Insulins
Breakup by Type:
- Short Acting
- Long Acting
Breakup by Application:
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
Breakup by Region:
- Southeast
- South
- Northeast
- North
- Central-West
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report offers an in-depth analysis of the competitive landscape, covering market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, a competitive dashboard, and a company evaluation quadrant. Additionally, detailed profiles of all major companies are included.
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: [email protected]
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-631-791-1145