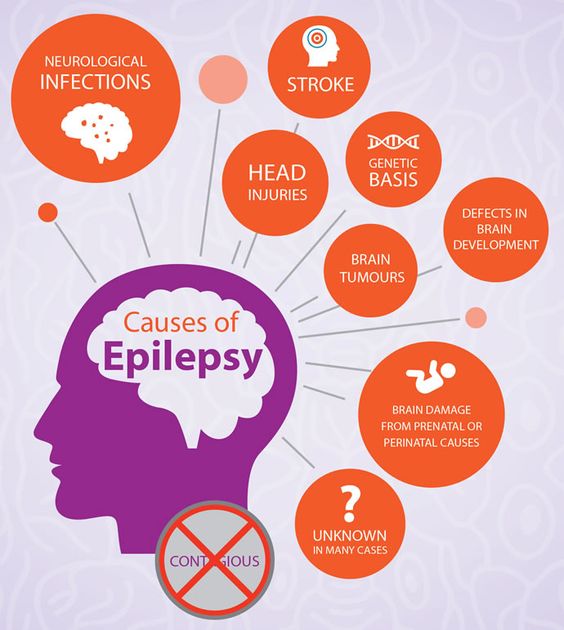
Recent advancements in epilepsy research from a neuroscientific perspective have brought about a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying this neurological disorder. Epilepsy, characterized by recurrent seizures, has long been a subject of intense investigation, with researchers delving into genetic, neuroimaging, and therapeutic domains to unravel its mysteries. This article provides an overview of cutting-edge research in epilepsy neuroscience, exploring the role of genetic factors, innovative neuroimaging techniques, novel therapeutic approaches, and insights from neural network studies. Additionally, we delve into the emerging understanding of neuroinflammation in epilepsy pathogenesis, discuss future directions in research, and address the ethical considerations and challenges that accompany advancements in this field.
Gabapentin 100 mg is a prescription medicine for the treatment of partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles, and restless leg syndrome. The active ingredient in the Gabapentin capsule belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants, which work on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves.
1. Introduction to Epilepsy and Neuroscientific Research
Overview of Epilepsy: Definition and Prevalence
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting millions worldwide.
Historical Context of Epilepsy Research
The study of epilepsy dates back centuries, with ancient beliefs ranging from divine possession to neurological underpinnings.
2. Genetics and Epilepsy: Unraveling the Role of Genetic Factors
Genetic Variants Associated with Epilepsy
Advances in genetic research have identified various gene mutations linked to epilepsy susceptibility.
Impact of Epigenetics on Epilepsy Development
Epigenetic mechanisms play a crucial role in modulating gene expression in epilepsy pathogenesis.
3. Neuroimaging Techniques in Epilepsy Research
MRI and fMRI Applications in Studying Epileptic Brain Activity
Modern imaging technologies provide insights into brain structure and function changes during epileptic episodes.
Advancements in EEG and MEG for Epilepsy Diagnosis and Monitoring
Electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) enable real-time monitoring of brain activity to aid in epilepsy diagnosis and treatment.
Gabapentin 300mg is a medication that contains gabapentin and is typically used to treat nerve pain and seizures. It works by modulating neurotransmitter release, which helps alleviate pain and control seizures. Physicians often prescribe it for conditions such as neuropathic pain, and post herpetic neuralgia, and as an adjunctive therapy for epilepsy.
4. Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Epilepsy Management
Emerging Pharmacological Treatments for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
Innovative drugs targeting specific molecular pathways offer promise for patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
Exploring Non-Pharmacological Interventions like Ketogenic Diet and Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Alternative treatments like the ketogenic diet and vagus nerve stimulation show potential in managing seizures and improving the quality of life for individuals with epilepsy.
5. Understanding Epilepsy Circuits: Insights from Neural Network Studies
Neuronal Network Dynamics in Epileptic Seizures
Epileptic seizures are like dance parties where the brain’s neurons get a little too excited and start firing off signals in a chaotic manner. Understanding these neural network dynamics is crucial in figuring out how to calm things down when the party gets out of control.
Role of Synaptic Plasticity in Epilepsy Pathophysiology
Think of synaptic plasticity as the brain’s ability to rewire itself like a master electrician rewiring a house. In epilepsy, this rewiring can sometimes go haywire, leading to abnormal connections and signaling patterns. By studying this process, researchers hope to unravel the mysteries of how epilepsy develops and progresses.
6. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Epilepsy Pathogenesis
Inflammatory Signaling Pathways in Epilepsy Development
When it comes to neuroinflammation in epilepsy, think of it as the brain’s immune system going into overdrive. This inflammatory response can contribute to neuronal damage and seizure activity. Understanding these signaling pathways is key to developing new treatment strategies that target inflammation to calm the brain’s storm.
Neuroprotective Potential of Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Epilepsy Treatment
Imagine anti-inflammatory agents as firefighters rushing in to put out the flames of neuroinflammation in the brain. Research is exploring the potential of these agents in protecting the brain from damage and reducing seizure frequency. It’s like giving the brain a soothing balm to help it heal.
7. Future Directions in Epilepsy Research: Potential Breakthroughs
Advances in Personalized Medicine for Epilepsy Management
Personalized medicine is like getting a tailored suit made just for you—it fits perfectly. In epilepsy, researchers are looking at how your unique genetic makeup and brain patterns can guide treatment decisions for better outcomes. It’s all about finding the right key to unlock the puzzle of your seizures.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Epilepsy Prediction and Treatment
AI and machine learning are like having a super-smart sidekick who can predict when trouble is brewing in the brain and suggest the best course of action. By analyzing huge amounts of data, these technologies hold the promise of revolutionizing how we predict and treat epilepsy. It’s like having a crystal ball for your brain.
8. Ethical Considerations and Challenges in Epilepsy Neuroscience
Ethical Implications of Brain Stimulation Technologies in Epilepsy Treatment
Brain stimulation technologies are like the brain’s own personal cheerleaders, nudging it towards healthier patterns. But with great power comes great responsibility—questions around safety, consent, and impact on personal identity are crucial considerations in using these cutting-edge therapies.
Addressing Data Privacy and Informed Consent in Epilepsy Research Studies
Data privacy and informed consent are like the bodyguards protecting your most valuable assets—your personal information and autonomy. In epilepsy research, ensuring that participants understand the risks and benefits of studies and that their data is handled with care, is a cornerstone of ethical practice. It’s about empowering individuals to make informed choices about their health journey. In conclusion, the strides made in epilepsy research through a neuroscientific lens offer promising avenues for improved diagnosis, treatment, and management of this debilitating condition. As researchers continue to unravel the intricate workings of the epileptic brain, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and transformative interventions looms on the horizon. By staying at the forefront of innovation and addressing ethical considerations, the field of epilepsy neuroscience is poised to make significant contributions to enhancing the quality of life for individuals living with epilepsy.