Introduction
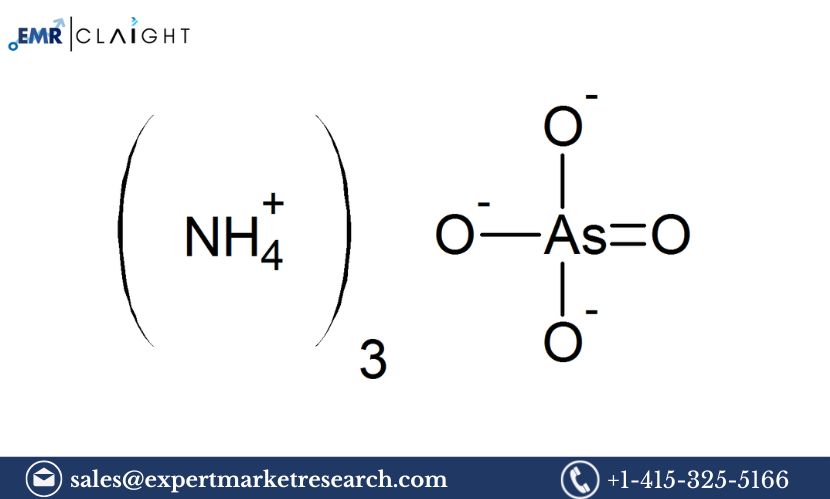
Ammonium Arsenite is an important inorganic compound, commonly used in various industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. This chemical is most notably employed as a pesticide and herbicide, as well as in some specialized chemical processes. Establishing an Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant involves careful planning and execution. A detailed project report provides essential guidance for investors, manufacturers, and businesses looking to enter this niche market. The Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report covers market trends, production processes, safety considerations, equipment, raw materials, and financial projections, creating a solid foundation for setting up the manufacturing unit.
Market Overview of Ammonium Arsenite
Ammonium Arsenite, although not as widely known as other chemicals, plays a significant role in several specialized industrial applications. The primary market for ammonium arsenite includes its use as a pesticide and herbicide, where it has been effective in controlling pests in crops, orchards, and gardens. However, due to its toxic nature, its usage is regulated, especially in developed nations, where safer alternatives have become more prevalent.
Despite these concerns, ammonium arsenite still holds a place in certain regions where its effectiveness in pest control is highly valued. Additionally, ammonium arsenite finds applications in industries like glass manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical research. As concerns regarding environmental safety continue to rise, the future market of ammonium arsenite will likely depend on the development of safer and more sustainable alternatives or more controlled applications within regulated frameworks.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Key Applications of Ammonium Arsenite
Ammonium Arsenite’s key applications make it useful across a variety of sectors:
-
Pesticides and Herbicides: Ammonium Arsenite is a key ingredient in certain pesticides and herbicides used for pest control in agriculture. It is particularly effective in combating insect pests and controlling weeds in crops and orchards.
-
Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, ammonium arsenite can be used in the preparation of certain medicines and formulations, particularly in the treatment of skin diseases and conditions.
-
Glass Manufacturing: Ammonium Arsenite is also used in the production of specialized glass, where it serves as an additive to enhance the properties of the final product.
-
Chemical Research: Due to its chemical properties, ammonium arsenite is utilized in various laboratory settings for research and experimentation. It is used in organic synthesis and as a reagent in some chemical reactions.
-
Tanning and Dyeing: It can be used in the tanning process of leather and in the dyeing of fabrics due to its chemical reactivity.
Although it is primarily used in specialized industries, ammonium arsenite remains an essential compound in the global chemical market.
Setting Up the Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant
Setting up an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires careful planning and attention to several key components: site selection, production processes, equipment, and safety standards. Below is an overview of each step involved in setting up the plant.
1. Location Selection
Choosing the right location for the manufacturing plant is crucial. The site should be close to the primary raw materials required for ammonium arsenite production, as well as to transportation infrastructure for easy access to markets. The site should also comply with local zoning and environmental regulations. Since ammonium arsenite is a toxic chemical, the location should be far enough from residential areas to minimize any safety risks.
2. Plant Layout and Design
The layout of the plant is essential for maximizing production efficiency while ensuring safety standards are maintained. The plant design should incorporate areas for raw material storage, production lines, storage for intermediate and final products, and waste management systems. Special attention should be paid to the safety measures required for handling toxic substances such as arsenic compounds.
The facility should also include sections for proper ventilation and fume extraction systems to ensure that workers are not exposed to harmful fumes. The layout should enable smooth material handling and efficient waste disposal processes.
3. Raw Materials and Feedstocks
The primary raw materials for manufacturing ammonium arsenite are arsenic trioxide (or arsenic pentoxide) and ammonia. Arsenic trioxide is a toxic and hazardous material, requiring careful handling and storage. The availability of high-quality arsenic trioxide and ammonia is essential for the consistent production of ammonium arsenite.
In addition to these primary raw materials, there may be other auxiliary chemicals or catalysts used in the process, depending on the specific production method chosen. It is essential to establish reliable suppliers for these materials to ensure consistent production without interruptions.
4. Equipment and Machinery
The manufacturing process of ammonium arsenite involves several critical stages, each requiring specialized equipment:
-
Reaction Vessels: Ammonium arsenite is typically produced by reacting arsenic trioxide with ammonia under controlled conditions. A high-quality, corrosion-resistant reaction vessel is essential to carry out this reaction safely.
-
Cooling and Condensation Systems: After the reaction, the product mixture needs to be cooled and condensed to separate ammonium arsenite from other by-products and solvents.
-
Filtration and Purification Systems: These systems are used to separate any impurities and ensure that the final product is of high purity. This is particularly important given the toxic nature of ammonium arsenite.
-
Packaging Equipment: The ammonium arsenite must be carefully packaged in airtight containers to prevent exposure to moisture and air, which could cause decomposition. The packaging must also comply with safety regulations to ensure safe handling and transportation.
-
Ventilation and Exhaust Systems: Since ammonium arsenite is toxic, adequate ventilation is essential to ensure that harmful fumes and gases are safely removed from the plant.
5. Production Process for Ammonium Arsenite
The production of ammonium arsenite involves the following steps:
-
Preparation of Raw Materials: Arsenic trioxide and ammonia are prepared and measured in appropriate proportions to ensure that the reaction proceeds efficiently.
-
Reaction: The raw materials are then reacted in a controlled environment. This typically takes place in a high-pressure reactor, where arsenic trioxide is mixed with ammonia to form ammonium arsenite. The reaction is highly exothermic, and temperature control is critical to prevent accidents.
Arsenic Trioxide (As₂O₃) + Ammonia (NH₃) → Ammonium Arsenite (NH₄AsO₂)
-
Cooling and Separation: The reaction mixture is cooled to facilitate the crystallization of ammonium arsenite. This is followed by filtration to remove any residual impurities.
-
Purification: The ammonium arsenite is then purified to ensure that it meets the required quality standards. This may involve additional washing or recrystallization steps.
-
Drying: The purified ammonium arsenite is dried to remove any residual moisture content.
-
Packaging: Finally, the ammonium arsenite is packaged in moisture-proof and air-tight containers to ensure its stability during storage and transport.
Safety Considerations in Ammonium Arsenite Production
Given the toxic nature of arsenic compounds, safety is a paramount concern in the production of ammonium arsenite. Some key safety measures include:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers handling ammonium arsenite and its raw materials must wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and respirators, to prevent direct contact and inhalation of toxic dust or fumes.
-
Fume Extraction and Ventilation Systems: The plant must be equipped with state-of-the-art ventilation and exhaust systems to ensure that no harmful gases or dust escape into the air. These systems help protect workers and the surrounding environment.
-
Emergency Response Procedures: The plant should have clear and comprehensive emergency response protocols in place for dealing with spills, leaks, or accidental exposure to arsenic compounds.
-
Hazardous Waste Management: Ammonium arsenite manufacturing generates hazardous waste, which must be managed and disposed of following strict environmental regulations. Proper waste disposal and recycling systems must be in place to minimize environmental impact.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Ammonium arsenite manufacturing plants are subject to strict regulatory guidelines due to the toxicity of the chemicals involved. Key regulations include:
-
Environmental Regulations: Compliance with local and international environmental protection laws is essential to ensure that toxic substances are managed responsibly. This includes ensuring that waste is safely treated and that emissions are minimized.
-
Occupational Health and Safety: Compliance with occupational health and safety regulations, such as those set by OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), is mandatory to protect workers from exposure to harmful chemicals.
-
ISO Certification: Adherence to ISO standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) ensures that the plant operates efficiently and meets global standards for production and safety.
Financial Planning and Investment
Establishing an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires substantial capital investment. The financial aspects to consider include:
- Capital Investment: This includes expenses for land, construction, machinery, equipment, and licensing fees.
- Operational Costs: Raw material procurement, labor, utilities, and maintenance costs form the core of operational expenses.
- Marketing and Distribution: Marketing and setting up distribution channels to reach target customers.
- Working Capital: Working capital is needed to cover day-to-day operational costs, such as raw material purchases, wages, and administrative expenses.
A detailed financial plan is crucial for understanding profitability and ensuring a sound return on investment (ROI).
Human Resources and Workforce Management
An ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires a skilled workforce to operate machinery, ensure quality control, and manage safety protocols. Key roles include:
- Plant Manager: Oversees overall operations, ensuring production runs smoothly and safely.
- Technicians: Operate and maintain equipment and machinery.
- Safety Officers: Monitor the adherence to safety protocols and manage emergency response plans.
- Quality Control Analysts: Ensure the final product meets required specifications.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Peter Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: [email protected]
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au