The Property and Casualty (P&C) sector has experienced a remarkable turnaround, flipping a $8.5 billion underwriting loss in Q1 2023 into a $9.3 billion gain in Q1 2024, with a combined ratio of 94.2%—below 100% indicates an underwriting profit. But in a constantly evolving market, staying ahead requires insurers to rethink their technology strategy and push the limits of innovation.
According to a Deloitte survey of 200 insurance executives, three out of four U.S. insurers are already leveraging Generative AI (Gen AI) in at least one business area, with claims processing and customer service leading the charge. However, scaling Gen AI adoption is not without its challenges. Data security, privacy concerns, and integration issues remain significant obstacles for insurers aiming to expand AI across their organizations.
While the opportunities are vast, so are the risks. There are compliance hurdles and operational vulnerabilities that must be managed carefully to fully tap into AI’s potential without compromising profitability or governance.
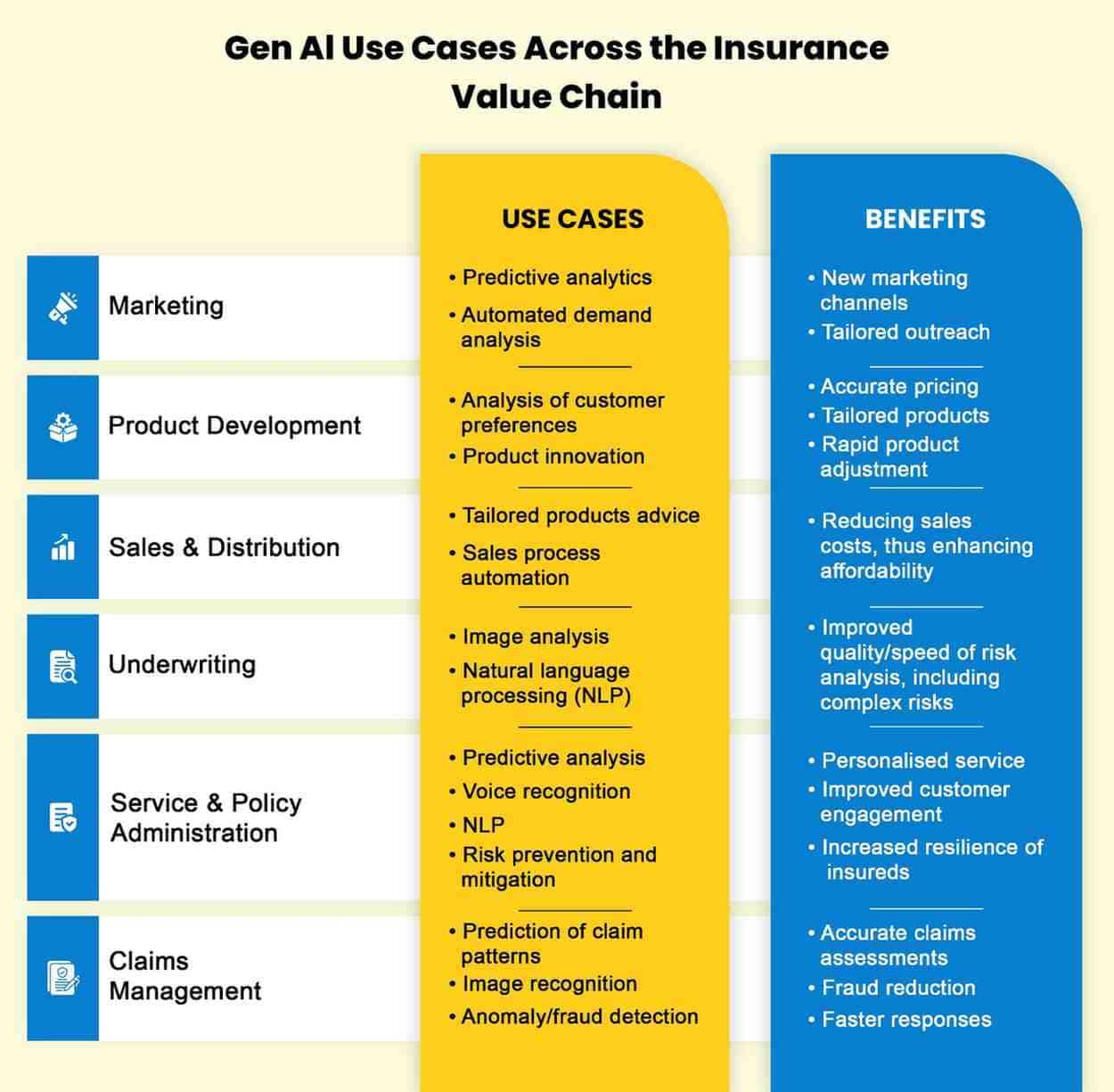
Gen AI in Insurance: Real Transformation in Operations
A 2025 Capgemini Research Institute report reveals that 67% of top-performing insurers are preparing to use Generative AI to enhance policyholder experiences and streamline operations.
Generative AI stands apart from traditional AI by creating new data and content, rather than just analyzing existing information or automating predefined tasks. Here are some key ways it’s transforming insurance:
-
Automating Policy Document Generation & Improving Claims Efficiency
One of the most impactful uses of Gen AI in insurance is automating the creation of policy documents. By inputting customer-specific data, AI generates customized policy documents that meet both regulatory standards and customer needs. This significantly reduces time and manual effort.
Additionally, Gen AI enhances productivity across the industry by supporting knowledge workers like underwriters, actuaries, claims adjusters, and engineers. It can also help summarize large volumes of information from the claims lifecycle, such as call transcripts and medical records, speeding up claims processing while improving accuracy.
-
Synthetic Data for Model Training
Generative AI allows insurers to simulate various risk scenarios using past data, creating realistic datasets that mimic real customer data. These simulated datasets help train machine large language models insurance in areas such as fraud detection and risk assessment, ultimately improving risk predictions and premium calculations.
-
Personalized Marketing Content
Insurers are increasingly using Gen AI to craft personalized marketing materials tailored to customer preferences. Whether it’s brochures, social media posts, or emails, AI can create content that resonates with different customer segments, driving engagement and increasing conversion rates.
Gen AI also supports direct customer communication by drafting service emails, policy updates, and automated messages, ensuring timely and relevant interactions throughout the customer journey.
-
Enhanced Customer Interactions
Some insurers have integrated Gen AI into customer service platforms to provide more natural, context-aware conversations. By analyzing past interactions and policy details, Gen AI can offer hyper-personalized responses, reducing the need for human intervention and significantly improving response times.
These examples highlight how Gen AI is not just an extension of traditional AI but a catalyst for innovation that enhances both operational efficiency and customer experiences.
Navigating the Risks of Generative AI in Insurance
While Generative AI offers numerous advantages, its integration into the insurance sector comes with several risks and challenges that must be addressed.
-
Model Hallucinations and Decision Integrity
Generative AI models are prone to generating outputs that seem plausible but are factually incorrect, known as “hallucinations.” In insurance, these inaccuracies can lead to faulty risk assessments, incorrect pricing, and erroneous claims decisions, which can undermine underwriting and claims processes.
To mitigate this, insurers are implementing safety checks and ensuring human oversight in AI-generated content, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of errors.
-
Adversarial Attacks and System Vulnerabilities
AI systems can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where bad actors input malicious data to manipulate the system. In insurance, this could result in fraudulent claims being approved or risk assessments being altered.
To safeguard against these risks, insurers need to employ strong security measures such as data encryption, secure model training practices, and adversarial testing. Regular audits and continuous monitoring of AI systems are also essential to protect against vulnerabilities.
-
Regulatory Compliance and Explainability
As AI adoption grows, regulators are increasing scrutiny on its use, particularly with regard to fairness and transparency. For example, Colorado is working on a framework to reduce bias in AI models used in underwriting and claims processing.
Gen AI models large language models insurance, often referred to as “black boxes,” can make it difficult to explain how decisions are made, which poses challenges for compliance with regulations that require transparency. Insurers must ensure that AI-driven decisions are interpretable, leveraging techniques like Explainable AI (XAI) to meet regulatory standards and maintain customer trust.
-
Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
Generative AI models large language models insurance, when trained on historical insurance data, can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases in the data. For instance, AI could reinforce unfair practices, such as offering lower coverage or higher premiums to certain demographic groups.
To combat this, insurers must adopt strategies such as retraining models on more diverse datasets, using bias detection algorithms, and performing regular audits of AI outcomes. Implementing fairness-aware machine learning techniques and maintaining human oversight can help ensure AI’s decisions align with fairness standards.
-
Operational Risks and Governance
Integrating Gen AI into insurance operations can introduce risks like system failures, data inaccuracies, and disruptions in processes. Insurers must establish robust governance frameworks with clear policies, accountability structures, and risk management protocols. Regular audits and compliance checks will help ensure that AI systems are operating within established guidelines.
For insurers to achieve meaningful results with Gen AI, they need a clear strategy and collaboration across cross-functional teams. Given the rapid evolution of Gen AI, seeking external expertise and partnerships can help navigate its complexities and mitigate risks.