How PV Panels Generate Electricity
Solar energy has gained immense popularity as a sustainable and renewable power source. Photovoltaic (PV) panels, commonly known as solar panels, are the primary technology behind harnessing sunlight and converting it into electricity. Understanding how PV panels generate electricity helps in appreciating the benefits and efficiency of solar power systems.
The Science Behind PV Panels
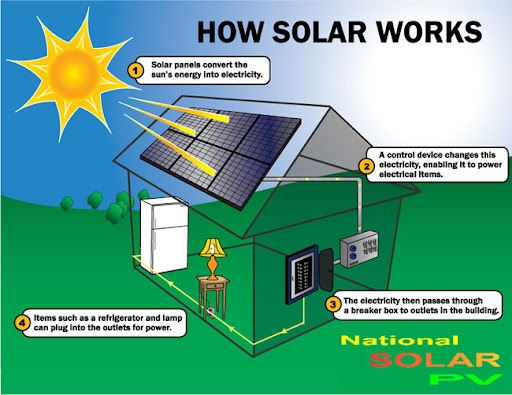
Photovoltaic panels generate electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon occurs when sunlight strikes the surface of a solar panel, exciting electrons within the semiconductor material, usually silicon. The movement of these electrons creates an electric current, which can then be used to power electrical appliances or stored in batteries for later use.
Components of a PV Panel
A standard PV panel consists of several key components that work together to generate electricity efficiently:
- Solar Cells – The fundamental unit responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
- Glass Covering – Protects solar cells from environmental factors like dust, debris, and moisture.
- Encapsulation Layer – Ensures the durability and longevity of solar cells.
- Conductive Wiring – Transfers the generated electricity from the solar cells to the inverter.
- Aluminum Frame – Provides structural stability and facilitates easy mounting.
Step-by-Step Process of Electricity Generation
- Sunlight Absorption
- When sunlight hits the PV panel, its energy is absorbed by the semiconductor material.
- Electron Excitation
- The absorbed energy excites electrons, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds.
- Electric Field Generation
- The panel’s internal electric field directs the free electrons towards conductive pathways.
- Current Flow
- The movement of electrons creates a direct current (DC), which is collected and transferred through the panel’s wiring.
- Conversion to Usable Electricity
- Since most household appliances run on alternating current (AC), an inverter converts the DC electricity into AC power.
- Power Distribution
- The converted electricity can be used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed into the power grid.
Efficiency Factors Affecting PV Panels
Several factors influence the efficiency of PV panels in generating electricity:
- Sunlight Intensity – The more sunlight a panel receives, the more energy it produces.
- Angle and Orientation – Proper positioning towards the sun maximizes energy absorption.
- Temperature – Excessive heat can reduce the efficiency of solar cells.
- Shading and Dirt Accumulation – Any obstruction reduces the panel’s ability to generate electricity.
Applications of PV Panels
PV panels are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential and commercial electricity generation
- Solar-powered streetlights and traffic signals
- Remote area power supply systems
- Agricultural water pumping solutions
- Charging stations for electric vehicles
Why Choose Solar Energy?
Switching to solar power offers numerous benefits:
- Renewable and Sustainable – Solar energy is an abundant and eco-friendly resource.
- Cost Savings – Reduces electricity bills and provides a long-term financial return.
- Energy Independence – Decreases reliance on fossil fuels and traditional power sources.
- Minimal Maintenance – PV panels have a long lifespan with minimal upkeep.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how solar panels work and how PV panels generate electricity highlights the significance of solar energy in today’s world. As technology advances, solar power continues to evolve, providing a cleaner, greener, and more efficient alternative to conventional energy sources. Investing in solar panels is not only beneficial for the environment but also for long-term energy sustainability.