Male breast pain is a common concern that can cause anxiety and discomfort. While some may immediately associate it with Gynecomastia Dubai, other conditions can also lead to breast tenderness or pain in men. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for proper management.
What Is Gynecomastia?
Definition and Causes:
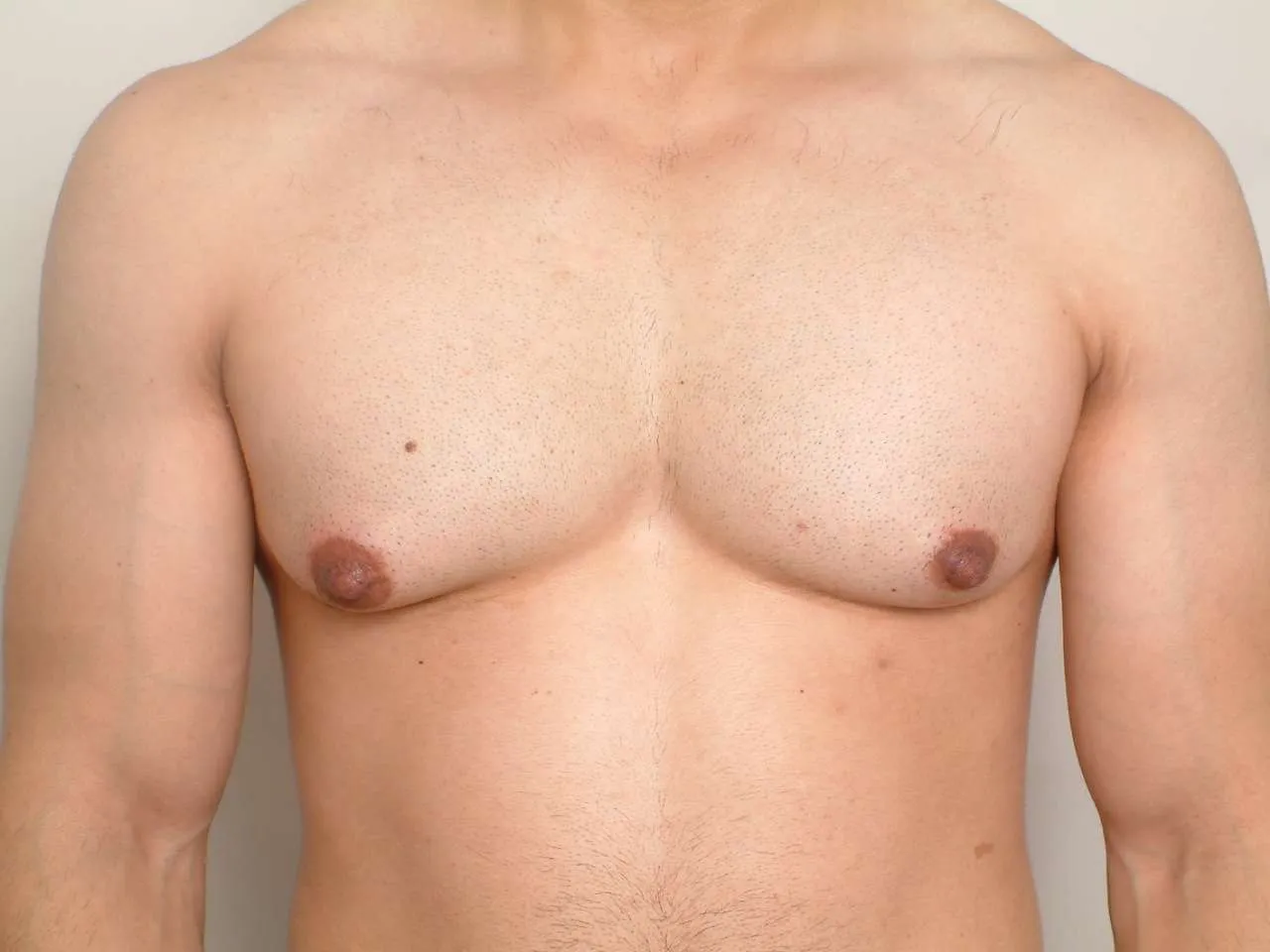
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. It is caused by an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels, leading to breast tissue growth. This condition can occur at any age and may be temporary or persistent.
Common Symptoms:
- Swollen breast gland tissue
- Tenderness or pain in the affected area
- A firm or rubbery mass beneath the nipple
Other Possible Causes of Male Breast Pain:
While gynecomastia is a well-known cause, other factors can contribute to breast pain in men. Identifying these can help in determining the right course of action.
Pseudogynecomastia:
Unlike gynecomastia, which involves glandular tissue growth, pseudo gynecomastia results from excess fat accumulation in the chest area. It is more common in individuals with higher body fat percentages and does not involve hormonal imbalance.
Muscle Strain:
Intense physical activity, especially weightlifting or chest exercises, can cause strain in the pectoral muscles. This strain may lead to pain or tenderness in the chest, sometimes mistaken for breast-related issues.
Hormonal Imbalance:
Fluctuations in hormone levels due to aging, medical conditions, or lifestyle changes can contribute to breast pain. Increased estrogen levels or decreased testosterone levels may cause discomfort and tissue changes in the chest.
Infections and Inflammation:
Conditions such as mastitis, an infection of the breast tissue, can cause redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. Infections may result from bacteria entering through cuts or injuries near the nipple area.
Cysts and Lumps:
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast tissue, leading to tenderness or pain. While most cysts are benign, any unusual lump should be evaluated to rule out more serious concerns.
Injury or Trauma:
Direct trauma to the chest, whether from accidents, sports, or physical impact, can lead to localized pain and swelling. The symptoms may persist for a few days or weeks, depending on the severity of the injury.
Medication-Induced Pain:
Certain medications, including those affecting hormone levels or metabolism, can contribute to breast tenderness. Consulting a healthcare professional about possible medication-related symptoms can be beneficial.
Nerve-Related Pain:
Nerve damage or conditions affecting the nervous system can sometimes cause sensations of pain or discomfort in the chest region. This type of pain may be sharp, tingling, or burning in nature.
Recognizing the Differences: Gynecomastia vs. Other Causes:
Understanding the key distinctions between Gynecomastia in Dubai and other causes of male breast pain can help with proper identification and management.
Gynecomastia Characteristics:
- Symmetrical swelling in both breasts, but can also be unilateral
- Firm, rubbery mass under the nipple
- Possible tenderness but no redness or warmth
Other Causes Characteristics:
- Pain associated with physical activity or trauma
- Soft fatty deposits rather than glandular tissue
- Redness, warmth, or other signs of infection in some cases
When to Seek Medical Attention:
While some causes of male breast pain may resolve on their own, certain symptoms may require medical evaluation.
Concerning Symptoms:
- Persistent or worsening pain
- Unexplained swelling or lumps
- Nipple discharge or changes in skin texture
- Signs of infection such as redness, warmth, or fever
Seeking medical guidance ensures that any underlying condition is addressed appropriately.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation:
A healthcare professional may conduct a thorough assessment to determine the cause of breast pain. This typically involves:
Physical Examination:
A doctor will check for lumps, swelling, tenderness, or any abnormalities in the chest area.
Hormone Level Testing:
Blood tests may be conducted to assess estrogen, testosterone, and other hormone levels that could be contributing to tissue changes.
Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Helps distinguish between glandular and fatty tissue.
- Mammography: May be used if a lump is detected to rule out other conditions.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments:
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage or prevent male breast pain, depending on the underlying cause.
Healthy Weight Management:
Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine can help reduce excess fat in the chest area, especially in cases of pseudogynecomastia.
Proper Exercise Techniques:
Avoiding overuse of chest muscles and allowing adequate recovery time after workouts can help prevent strain-related pain.
Medication Awareness:
Being mindful of medications that may contribute to breast pain and discussing alternatives with a healthcare provider can be beneficial.
Regular Health Checkups:
Routine medical checkups help in the early detection of hormonal imbalances or other health concerns that may lead to breast pain.
Conclusion:
Male breast pain can be caused by various factors, including gynecomastia, muscle strain, infections, or hormonal changes. Understanding the symptoms and underlying causes is essential for proper identification and management. If pain persists or is accompanied by unusual symptoms, seeking medical attention is recommended to ensure the best course of action.